Wastewater
Wastewater is the used water from households and business, which is disposed through the sewerage syastem. The majority of the wastewater is sourced from showers and washing machines.
As we know, water resources on earth are limited so that top priority has been given to the waste water treatment, which can provide a sustainable and secure water resource to human being.
Therefore, regulatory frameworks, which includes social constructs, policy, legislation, and so on need to be taken into consideration. From my own perspective, legislation framework plays a significant role in developing a better wastewater engineering.
The relationship between legislation framework and wastewater engineering
Speaking of the relationship between legislation framework and wastewater engineering, I think they are complementary, which means legislation framework seems to be a constraint in order to supervise the quality of the wastewater and wastewater treatment engineering can be improved with the development of the legislation framework in order to make sure the healthy human body, energy-consuming reduction, and work efficiency improvement.
The importance of regulation in the development of better wastewater engineering
To be clarified, regulation or legislation of wastewater is provided by the federal government, which presents and summarizes recommended wastewater treatment guidelines for the development of better wastewater engineering in order to protect ecosystems and environment in a sustainable way.
In addition, there is an old saying goes that nothing can be accomplished without norms or standards. Similarly, wastewater treatment is the most important issue related to people’s healthy life under the wastewater regulation or legislation, which can promote the development of the wastewater engineering.
Only on the basis of obeying the regulation or legislation, wastewater engineering can be better development in a sustainable way. Therefore, regulation or legislation of wastewater can do a great job in developing wastewater life cycle (shown in Figure 1 below) [1]. The figure demonstrated that five effective regulatory cycle at different stages will make sure wastewater engineering proceeding smoothly.
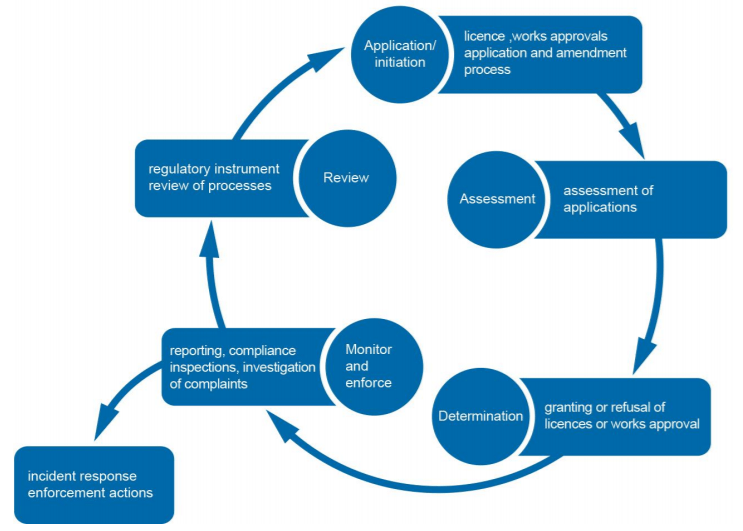
Additionally, with the help of the regulation or legislation, the final results of the wastewater engineering will reach a higher hierarchy (shown in Figure 2 below) [1].
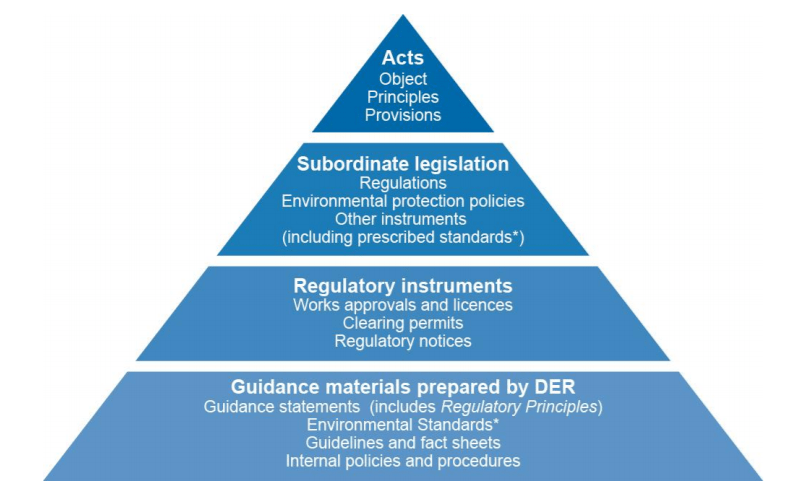
What’s more, I found some Australian regulations, which can illustrate how to have an important influence on the following aspects:
- Metropolitan Arterial Drainage Act (1982) provides for an arterial drainage scheme and the declaration of drainage courses in order to regulate the wastewater treatment [2].
- The clearing of vegetation is controlled under Environmental Protection Act (1986) and Country Areas Water Supply Regulations (1981), which are used to manage and protect salinization of water resources from wastewater treatment in factories [3].
- The Department of Wastewater and Environmental Regulation leads wastewater resource management in Western Australia by coordinating cross-government efforts to protect and manage wastewater resources (Water Agencies Act, 1984), including [4]:
- assessing wastewater resources;promoting the efficient use of wastewater resources;
- promoting the efficient provision of wastewater services;
- preparing plans for and providing advice on wastewater management;
- The objects include providing for the sustainable use and development of wastewater resources, protection of their ecosystems and the environment in which assisting the integration of wastewater resources management with other natural resources management.
- The wastewater treatment should be associated by-laws in order to protect the state’s public drinking water sources, i.e. proclaimed catchment areas, water reserves and pollution areas (underground water pollution control areas).
Finally, wastewater regulation or legislation in Western Australia is currently contained in six separate Acts, several of which were established in the early 20th century. Constant amendments to the wastewater regulation or legislation over the decades has already become more completed, and in some cases, wastewater regulation or legislation has a positive influence on modern wastewater engineering management.
Innovative legislation as solution to wastewater engineering related to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals)
Old legislation cannot provide for management of innovative new ways to manage wastewater. From my own perspective, innovative regulation or legislation related to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) should be created as solution in order to cope with the wastewater engineering issues:
- First of all, education occupied the significant role in wastewater engineering, which means more and more people should be conscious of the importance of the wastewater for the sake of avoiding and reducing the wastewater produce in daily life, including bathing and washing. According to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Clause 4.7 (shown in Figure 3 below) [5], By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development. This is exactly what the contemporary society needs. Therefore, the innovative legislation should be enacted, which will invest more money to the education in order to increase public awareness of wastewater treatment, and also it’s a great way to make sure public grasping basic wastewater knowledge as well as achieving sustainable development of wastewater in the years to come.

- Secondly, it is known that upgrading of equipment will decide the wastewater treatment energy-consumption and efficiency. According to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Clause 9.4 (shown in Figure 4 below) [5], By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, with all countries taking action in accordance with their respective capabilities. Therefore, legislative provisions also should cater for equipment upgrading of wastewater treatment by investing a large amount of money on small and medium-sized enterprises, which means government will not worry about water quality issues in the future.

- Thirdly, wastewater treatment cycle at different stages (mentioned above) will improve water quality, which can make sure wastewater engineering proceeding smoothly. According to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Clause 6.3 (shown in Figure 5 below) [5], By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally. Therefore, an innovative legislation should be created in order to reduce pollution, improve untreated wastewater, and focus on increasing recycling and reusing wastewater globally.

- Finally, the development of wastewater engineering is closely related to cutting-edge technologies. According to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Clause 9.5 [5], Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries, in particular developing countries, including, by 2030, encouraging innovation and substantially increasing the number of research and development workers per 1 million people and public and private research and development spending. Therefore, government should carry out a legislation about developing the cutting-edge technologies. An example of a new approach to manage water is managed aquifer recharge. This is the injection of recycled water into groundwater where it can be stored for later use (shown in Figure 6 below) [6]. Construction is underway to build Australia’s first full scale groundwater replenishment scheme. When complete, the scheme will have the capacity to recharge 14 billion litres of recycled water per year into deep confined aquifers, providing an additional secure, rainfall independent water source for Perth in order to reduce the stress of wastewater treatment.

The innovative legislation closely related to SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) will support the development of better wastewater engineering in order to reduce the wastewater pollution, increase water quality, protect the environment, and even change climate in Perth or in Western Australia or maybe all over the world.
Reference
[1]https://www.der.wa.gov.au/images/documents/our-work/regulatory-principles/Guidance_Statement_Regulatory_Principles.pdf
[2]https://www.legislation.wa.gov.au/legislation/prod/filestore.nsf/FileURL/mrdoc_25638.pdf/$FILE/Metropolitan%20Arterial%20Drainage%20Act%201982%20-%20%5B03-a0-03%5D.pdf?OpenElement
[3]https://www.legislation.wa.gov.au/legislation/prod/filestore.nsf/FileURL/mrdoc_41689.pdf/$FILE/Environmental%20Protection%20Act%201986%20-%20%5B09-c0-02%5D.pdf?OpenElement
[4]http://www.water.wa.gov.au/legislation/current-legislation
[5]https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/
[6]http://www.water.wa.gov.au/legislation/water/water-resource-management-legislation