What kinds of issues do wastewater infrastructure facing?
A variety of issues need to be taken into consideration into wastewater infrastructure: 1. Aging wastewater infrastructure 2. Funding concerns 3. Expanding regulations 4. Technology backwardness
Aging wastewater infrastructure
It is beyond any question that the most important issue currently facing wastewater infrastructure is aging wastewater infrastructure, which includes pumps, pipelines, tunnels, and wastewater treatment facilities (shown in Figure 1 below).
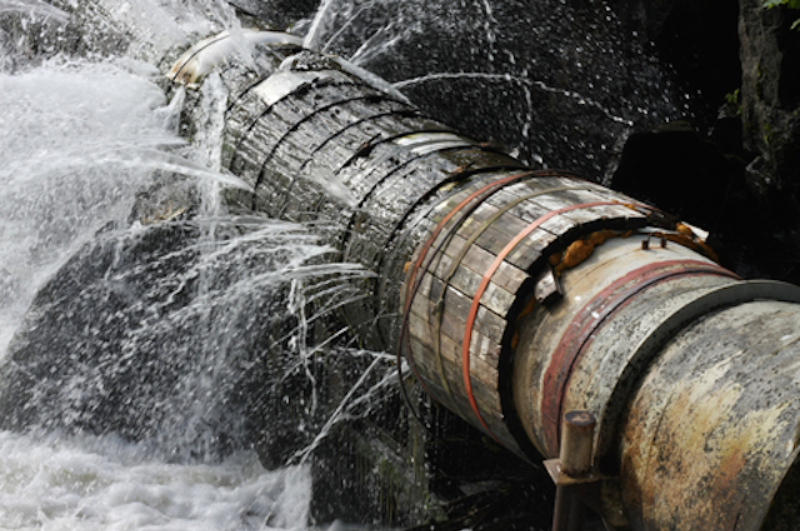

The seriousness of this problem is that aging wastewater infrastructure will lead to wastewater not to be treated very cleanly, which will pose a potential threat to human health as well as natural environment. In addition, it will not catch up the up-to-date regulation, which is illegal and constitute a crime. What’s more, keeping using the aging wastewater infrastructure will have a negative influence on energy consumption due to the fact that innovative technology cannot be applied into aging wastewater infrastructure.
For example, more than 50% of the water distribution and collection systems in the Northeastern America are more than 60 years old. In the Midwest of America, 35% of water processing infrastructure is more than 60 years old [2].
Based on the SDG 9 (sustainable development goals 9) (shown in Figure 2 below): In 2016, medium-high and high-tech sectors accounted for 44.7 percent of the global manufacturing value added. Medium-high and high-tech products continued to dominate manufacturing production in Northern America and Europe, reaching 47.4 percent in 2016 compared with 10.4 percent in least developed countries [3]. Even if America nominated the medium-high and high technological products in the world, reaching at 44.7%, aging wastewater infrastructure occurs commonly in America. Not to say that the serious problems of aging wastewater infrastructure occur in developing countries, such as China, India, and so on.

In my opinion, Funding (Money) is always a problem in solving the aging wastewater infrastructure, which will use to purchase the up-to-date machines supported by government keeping up with the changing regulations and technology in the future.
What should we do with aging wastewater infrastructure?
Based on the analysis mentioned above, top priority has been given to the solution of dealing with aging wastewater infrastructure. We need to evaluate the existing wastewater equipment and to determine that we can purchase as well as update wastewater equipment or repair the existing wastewater equipment adding innovative technology in order to reduce money to update aging wastewater equipment to a larger extend. There are several factors acting as solution of aging wastewater infrastructure. Some factors to be considered include:
- First of all, we need to appeal to the government focusing on the aging wastewater infrastructure, which will be our support for funding. No matter refurbishment or replacement, we need a lot of money to deal with the problem.
- Secondly, laws and regulations must be observed when we are working on wastewater treatment so that aging wastewater infrastructure should be solved.
- Thirdly, we need to consider the condition of the aging equipment, which is a significant element in the determination of whether the aging wastewater infrastructure can be refurbished or requires replacement under government financial support as well as law permission.
- Finally, advanced science and technology (including cloud computing, virtualization and hosted application) are indispensable, which will invent new machines to do the wastewater treatment and develop the new method to improve the existing wastewater equipment in order to reduce energy consumption, costs and risk to a larger extent in an sustainable way.
Innovation
In class, Dr. Steve Capewell develop the idea of innovation across the water cycle, which is quite inspiring and useful (shown in Figure 3 below).
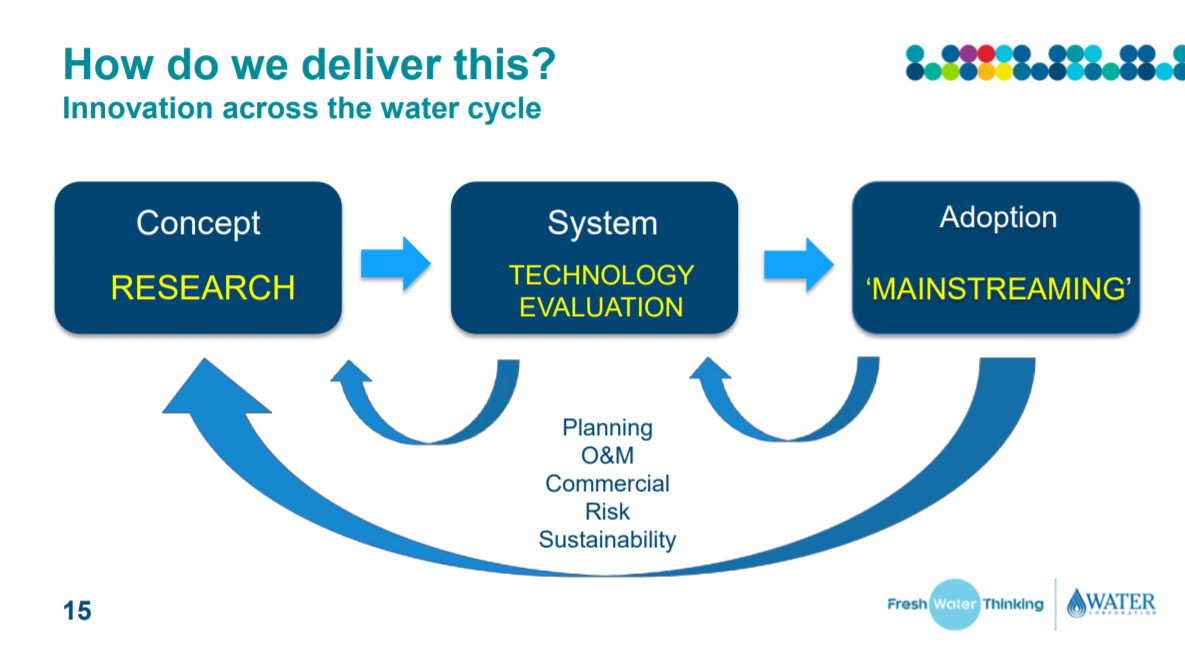
It shows that innovation can apply in different stages of water cycle, which contains concept, system and adoption under the consideration of commercial, risk, sustainability and so on. Based on the concept map mentioned by Dr. Steve Capewell, aging wastewater infrastructure belongs to second and last stage, which needs to technology evaluation and mainstreaming under the commercial, risk and sustainable consideration. Under this circumstance, I will do the further analysis of the aging wastewater infrastructure associated with SDG 9 (shown in Figure 4 below).

- we need to conduct vigorous propaganda the harm of wastewater and aging wastewater infrastructure for public in order to increase the awareness of environmental protection. This is the most effective and economic action to reduce wastewater generation.
- Upgrading and retrofitting aging wastewater infrastructure need to be more considered to make sustainable environment with advanced and resource-used efficient technologies all over the world according to SDG 9, clause 9.4 [3].
- Scientific research needs to be taken into consideration, which will upgrade the technological capabilities of aging wastewater infrastructure in the future. In particular, the developing countries should be encouraged to increase the number of researches for the sake of doing more innovative technology on aging wastewater infrastructure. For example, we need to encourage innovation and develop workers per 1 million people and public and private research, which is associated with SDG 9, clause 9.5 [3].
- Due to the backward innovative technology (aging wastewater infrastructure) in the developing countries, the water pollution has become a severe problem in the developing countries so that they cannot acquire the clean water. Most developed countries grasp the core technology of upgrading the aging wastewater infrastructure compared to the developing countries. Therefore, developed countries have responsible to enhance developing counties (African countries) financial and technological support (SDG 9, clause 9.A.) [3] in order to make the world a better place. For example, it is significant that the developing countries need to increase the access to advanced technological information and communications through Internet provided by developed countries in 2020 (SDG 9, clause 9.C) [3].
Reference
[2] Prosser MEE, Speight VL, Filion YR. Life‐cycle energy analysis of performance versus age‐based pipe replacement schedules. Water Works 2013, 105: P721– P732.
[3] https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg9
[4] Dr. Steve Capewell, Water Corporation. The future for urban water services. P15.